The stage is being set for a massive global rice shortage
09/15/2022 / By News Editors

This wasn’t supposed to happen. For months, I have been writing article after article about the rapidly growing global food crisis, but even though drought is devastating so many other crops all over the planet I thought that there would be plenty of rice in 2023. Unfortunately, I was wrong. As you will see below, some of the biggest rice producers in the entire world are being hit really hard, and rice production is going to be way below expectations this year. Of course rice is one of the primary staples that poor nations depend upon, and so this is a really big deal. If there is a serious shortage of rice in 2023, that is going to have enormous implications for all of us.
(Article by Michael Snyder republished from TheEconomicCollapseBlog.com)
An announcement that India just made should be front page news all over the globe right now.
India usually accounts for over 40 percent of all worldwide rice shipments, but now they have placed severe restrictions on all future exports this year…
India banned exports of broken rice and imposed a 20% duty on exports of various grades of rice on Thursday as the world’s biggest exporter of the grain tries to augment supplies and calm local prices after below-average monsoon rainfall curtailed planting.
India exports rice to more than 150 countries, and any reduction in its shipments would increase upward pressure on food prices, which are already rising because of drought, heat-waves and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Did you catch that last sentence?
150 different nations depend on rice from India.
So where are they going to get their rice?
Normally, India exports more rice than the next four largest exporters combined…
India’s rice exports touched a record 21.5 million tons in 2021, more than the combined shipments of the world’s next four biggest exporters of the grain: Thailand, Vietnam, Pakistan and the United States.
Europe certainly isn’t going to make up the difference.
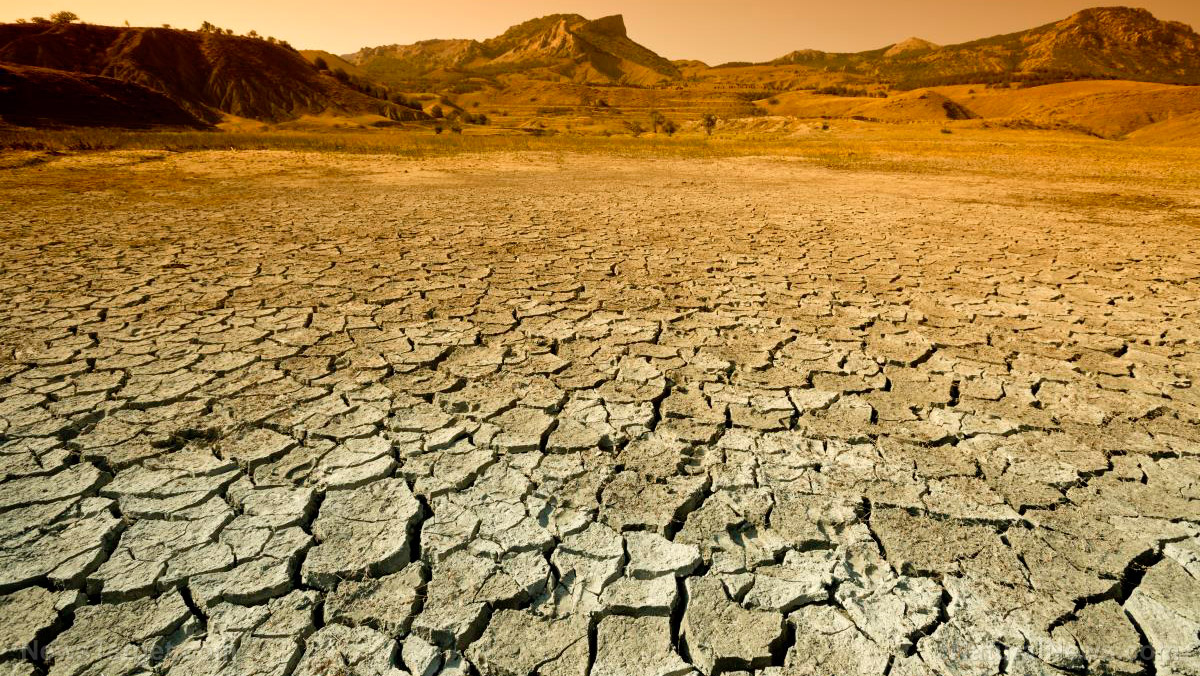
Italy is the biggest rice producer in the European Union, and it is being projected that rice production in that nation will be down about 30 percent this year due to the endless drought that Europe is currently experiencing…
The unfavorable weather has already taken a serious toll on the rice industry. Estimates say farmers are expecting to lose around 30 percent of their yields this year, and the industry has already hemorrhaged around $3 billion as a result of the drought. Many of the most stricken fields are in the regions of Lombardy and Piedmont, which together produce around 90 percent of Italy’s rice.
Rice production is going to be way down in the United States as well.
California usually produces about 20 percent of all U.S. rice, but this year a severe lack of water for agricultural purposes is making things exceedingly difficult for rice growers in the state…
Rice farmers in Colusa County, 60 miles north of Sacramento, received 18% of the federal water shipments to which they are entitled, far less than normal and too little for many to grow the crop at all.
“Even in a drought, rice farmers have been able to get a fairly high percentage of the water they had rights to,” said Tim Johnson, chief executive of the California Rice Commission. “Now they are experiencing drought at a level they’ve never seen before.”
What we are witnessing is truly unprecedented.
I know that this may be hard to believe, but it is being reported that “about 300,000 out of the 550,000 acres committed to rice growing in California will go without harvest” in 2022. The following comes from Zero Hedge…
New satellite imagery shows a large swath of California’s rice fields has been left barren without harvest as fears of a ‘mini dust bowl’ emerge due to diminishing water supplies.
Kurt Richter, a third-generation rice farmer in Colusa, the rice capital of California, told San Francisco Chronicle that fields upon fields of the grain have already transformed into a “wasteland.”
A report via the US Department of Agriculture shows about 300,000 out of the 550,000 acres committed to rice growing in California will go without harvest. This could potentially drive up sushi prices nationwide because most of the rice produced in the state is for just that.
Of course many other crops are being hit extremely hard as well.
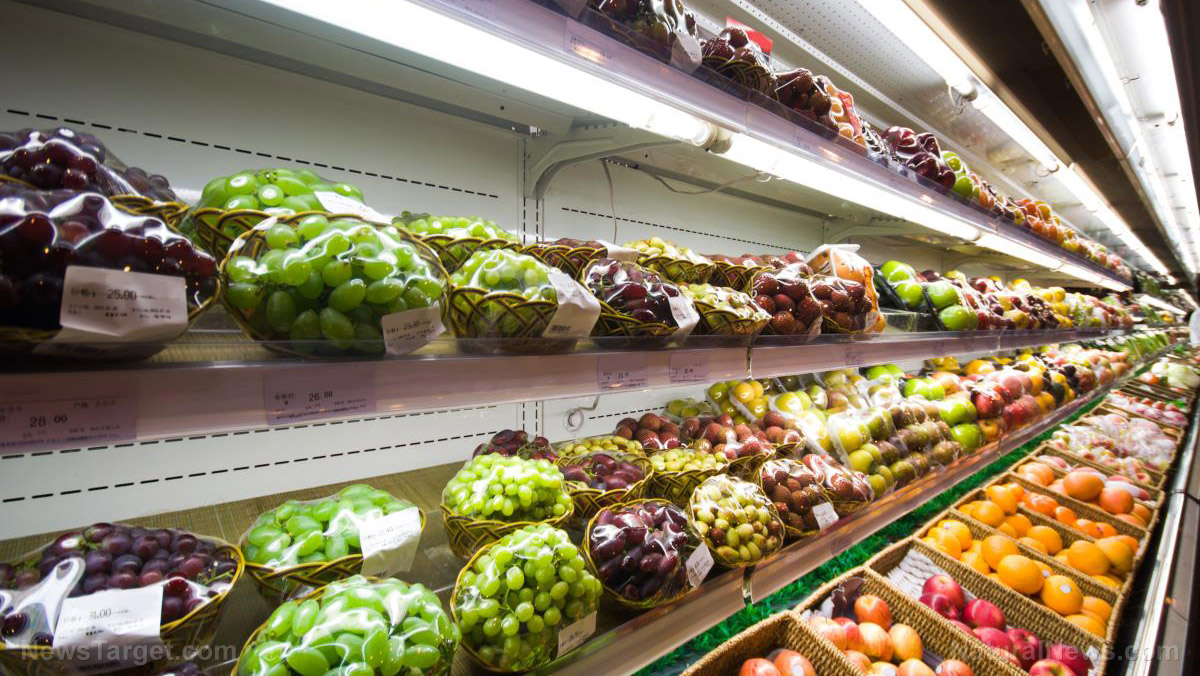
California normally produces approximately a third of our vegetables and about two-thirds of our fruits and nuts, and the lack of production this year is already starting to show up on our store shelves…
High temperatures in the Western U.S. are hitting the produce industry, damaging crops, shrinking shipments, and leaving fewer leafy greens and fruits on supermarket shelves.
A California grower said some of his lettuce leaves are turning brown and melting in the fields because of crop diseases intensified by the high temperatures. In Pennsylvania, a retailer said its stores went a week without having strawberries to sell. A New York distributor has substituted honeydew melons for watermelons, which have become scarce.
Supermarkets say they are giving less shelf space to products with weather-induced discolorations, bruises or burns. Stores are cutting prices on poor-quality items to avoid getting stuck with them, and increasingly receiving products from Canada, Florida, New Jersey and Ohio instead of California, long the go-to source for U.S. grocers.
This crisis is only going to get worse in the months ahead.
I have been encouraging my readers to get prepared for a very long time, and I hope that you have taken that advice.
All over the planet, agricultural production is going to be way below original projections this year. For example, just check out what is happening to olive oil production in Spain…
In July, temperatures broke records to top 40 degrees Celsius (104.5 degrees Fahrenheit) across parts of France, Spain, Italy and Portugal. By early August, sweltering heat and a lack of rainfall had pushed almost two-thirds of land in the European Union into drought conditions, according to the European Drought Observatory.
Olive oil producers have been hit hard. Kyle Holland, a pricing analyst for oilseeds and grains at Mintec, a commodities data company, expects a “dramatic reduction” of between 33% and 38% in Spain’s olive oil harvest that begins in October.
Spain is the world’s biggest producer of olive oil, accounting for more than two-fifths of global supply last year, according to the International Olive Council. Greece, Italy and Portugal are also major producers.
For a lot more data points on the rapidly growing global food crisis, please see my previous article entitled “A List Of 33 Things We Know About The Coming Food Shortages”.
None of us have ever faced anything like this.
The food that will not be harvested in the months ahead will not be on our store shelves in 2023.
Food prices are going to rise to absolutely ridiculous levels, and the head of the UN is already warning of “multiple famines” next year.
This is not a drill. Food shortages really are coming, and our world will be changing in wild and unpredictable ways.
Read more at: TheEconomicCollapseBlog.com
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
agriculture, chaos, climate, collapse, crops, disaster, drought, famine, food collapse, food scarcity, food supply, grocery, harvest, hunger, panic, products, rationing, rice shortage, starvation, supply chain
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
FoodScarcity.News is a fact-based public education website published by CORONA2019 News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2022 by Food Scarcity News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.